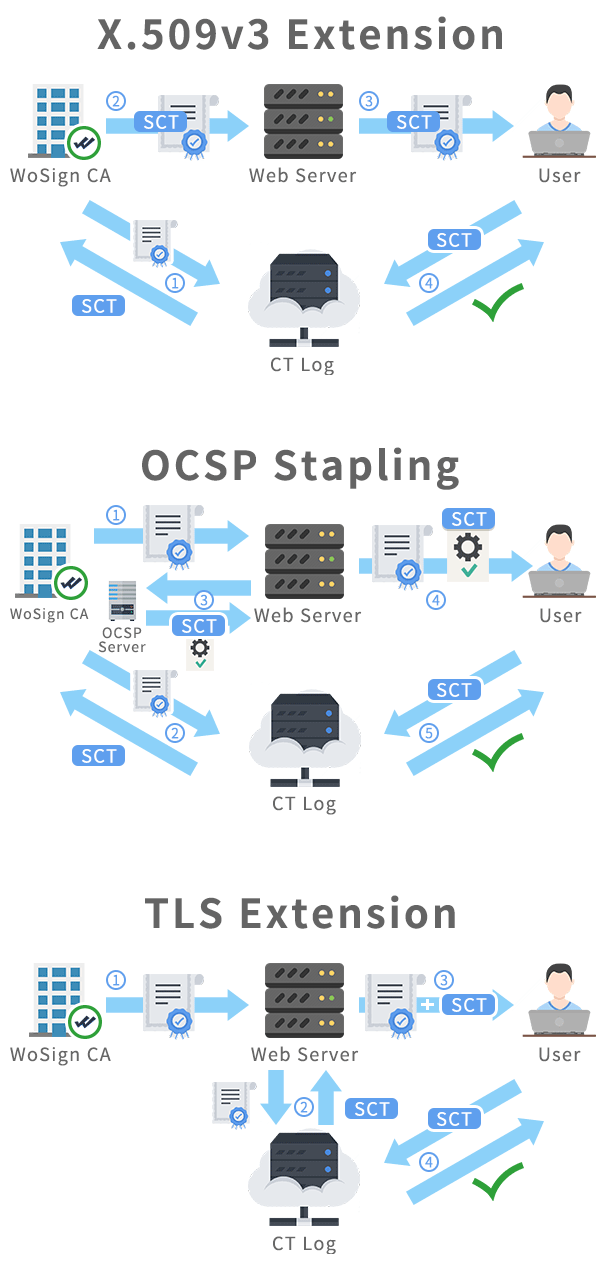
WoSign log all issued SSL certificates to public CT log servers
2016-07-04WoSign, the No. 1 SSL certificate market share CA (Certificate Authority) in China, and a leading global CA and provider of trusted identity and authentication services, announces the logging of all SSL certificates it issues to the public Certificate Transparency (CT) log servers starting today. All issued SSL certificates will contain the special embedded SCT data necessary to verify the log submission. With this, WoSign demonstrates transparency which is not only beneficial to WoSign’s worldwide subscribers, but also beneficial to all Internet security stakeholders, such as domain owners, certificate authorities, and browser manufacturers, who have a vested interest in maintaining the health and integrity of the WoSign SSL certificate system.
This implementation is stricter than Google Chrome's current requirements which applies today only to Extended Validation (EV) SSL certificates; WoSign will log all issued SSL certificates to at least 3 public CT log servers and embedded the SCT data into the certificates, demonstrating true transparency.
For browsers, if any SSL certificate issued by WoSign after July 5th, 2016 that don’t include SCT data, browsers can distrust this SSL certificate and report to us as an incident. For WoSign customers, if you find the SSL certificate don’t include the SCT data, then you can refuse to accept it and ask for re-issuance or ask for refund, including free SSL certificate and charged certificate, including DV SSL, IV SSL, OV SSL and EV SSL certificate.
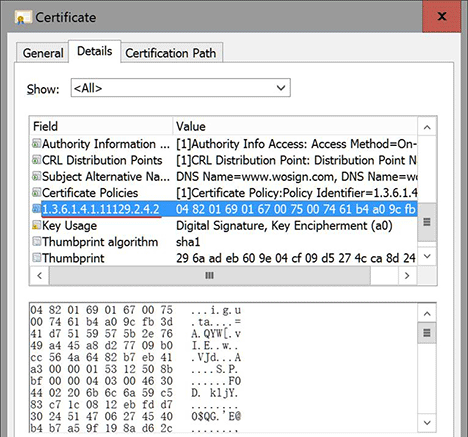
Google's Certificate Transparency project fixes several structural flaws in the SSL certificate system, which is the main cryptographic system that underlies all HTTPS connections. These flaws weaken the reliability and effectiveness of encrypted Internet connections and can compromise critical TLS/SSL mechanisms, including domain validation, end-to-end encryption, and the chains of trust set up by certificate authorities. If left unchecked, these flaws can facilitate a wide range of security attacks, such as website spoofing, server impersonation, and man-in-the-middle attacks.
Certificate Transparency strengthens the chains of trust that extend from CAs all the way down to individual servers, making HTTPS connections more reliable and less vulnerable to interception or impersonation. But what’s more, as a general security measure, Certificate Transparency helps guard against broader Internet security attacks, making browsing safer for all users.